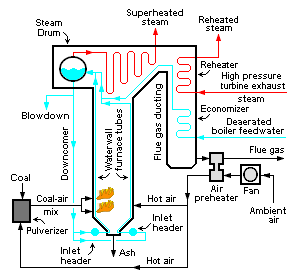
What is a steam boiler?
A boiler or a steam boiler in simple words is a device used to generate the steam at a desired pressure and temperature by transferring heat energy which is generally produced by burning fuel in order heat the water to change it to steam. The steam used in the boiler is used for external purposes i.e. electricity generation, heating or other industrial purposes.
Anther definition of boiler can be that Boiler means a pressure vessel in which steam is generated for use external to itself by application of heat which is wholly or partly under pressure when steam is shut off.
A complete boiler system can be defined as combination of apparatus used for producing, furnishing or recovering heat together with the apparatus for transferring the heat so made available to the fluid being heated and vaporized.
Formula for Steam Boiler Efficiency
Efficiency of any boiler can be expressed as the percentage of total heat exported by outlet steam in the total heat supplied by the fuel i.e.
Steam Boiler Efficiency (%) = Heat Exported by Outlet Steam x 100 / Heat Supplied by the Fuel
This value includes thermal efficiency, combustion efficiency & fuel to steam efficiency. In general Steam boiler efficiency depends upon the size of boiler and fuel used. Well known efficiency of steam boiler is 80% to 88% which is due to many heat losses that may include incomplete combustion, radiation loss from steam boiler surrounding wall, defective combustion flue gases.
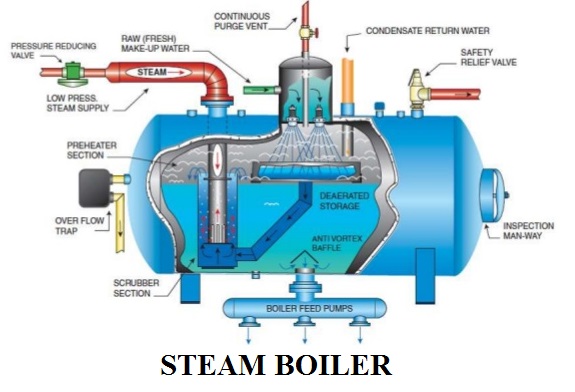
Basic Function of a Boiler
As the name states the function of a steam boiler is very simple i.e. generating, storing and distributing the steam. The fluid is contained in the boiler drum called shell and the thermal energy released during combustion of fuel is transferred to water and this converts water into steam at the desired temperature and pressure.
Types of Steam Boilers
- Fire Tube Boilers: Relatively small steam capacities(12,000 kg/hour). Low to medium steam pressures(18 kg/cm2). Operates with oil, gas or solid fuels.
- Water Tube Boilers: Used for high steam demand and high pressure requirements. Capacity range of 4,500– 120,000 kg/hour. Combustion efficiency of water tube boiler is enhanced by induced draft air provisions. These boilers need good quality water and needs water treatment plant for maintaining the required water quality for boilers.
- Packaged Boiler: Provide high heat transfer, faster evaporation, good convective heat transfer. Good combustion efficiency and high thermal efficiency. Classified based on number of passes.
- Stoker Fired Boiler: Uses both suspension and grate burning. Coal fed continuously over burning coal bed. Coal fines burn in suspension and larger coal pieces burn on grate. Good flexibility to meet changing load requirements. Preferred over other type of stokers in industrial application. Sub categorized in Spreader stokers and Chain-grate or traveling-grate stoker.
- Pulverized Fuel Steam Boilers: Pulverized coal powder blown with combustion air into boiler through burner nozzles. Combustion temperature at 1300 -1700°C. Some of the benefits are varying coal quality, quick response to load changes and high pre-heat air temperatures. Coal is pulverized to a fine powder, so that less than 2% is +300 microns, and 70-75% is below 75 microns. Coal is blown with part of the combustion air into the steam boiler plant through a series of burner nozzles.
- Waste Heat Boiler
- Fluidized Bed (FBC) Boiler
Applications of steam boilers
There are many uses of boilers which can be mainly categorized in following classes.
Boilers for Power generation: There are opportunities for generating the power using the steam from a boiler this power can be either mechanical or electrical so the example of mechanical power is steam engine and example of electrical power is steam turbine which uses steam to produce mechanical power and then to generate electricity.
Heating is another important use of steam generated through boilers, which is used for heating residential and industrial buildings in cold weather and for producing hot waters for hot water supply.
Boilers for industrial processes: Steam is usually used for industrial processes such as for sizing and bleaching etc. in textile industries and other applications like sugar mills, cement plants, agricultural and chemical process industries.
Selection of a Steam Boiler
Industrial boilers are very important part of any industry where these are used. These sometimes become cause of major accidents when mishandled or over pressured. Below are some factors which should be considered for selection of boilers in order to achieve safe working atmosphere and reliability of boiler systems.
- The working pressure and quality of steam required: The boiler should generate maximum amount of steam at a required pressure and temperature and quality with minimum fuel consumption and expenses
- Steam generation rate should be as per requirements of intended use, an extra over designed or under designed boiler is not a good choice. A good boiler system must be able to cope up with fluctuating demands of steam supply.
- Floor area availability should be sufficient for maintenance and operation of a steam boiler. In addition accessibility for repair and inspection should be major factor in selection of a steam boiler and available place or space.
- Erection facilities: It should be absolutely reliable, light in weight, should not occupy large space. Steam Boiler should be capable of quick starting and conforming to safety regulations. The boiler components should be transportable without difficulty and its installation should be simple.
- The portable load factor
- The fuel and water availability
- Operating and maintenance costs: All parts and components of steam boiler should be easily accessible for inspection, repair and replacement. The tubes of the boiler should not accumulate soot or water deposits and should be sufficiently strong to allow for wear and corrosion. The water and gas circuits should be such as to allow minimum fluid velocity (for low frictional losses).
Fire Steam Boiler Animation Video Explanation