What is a Gear Motor? Gear motor is a special type of electrical motor. The main purpose of gear motor is to produce high torque while using a low horsepower, or low speed, motor output.
You can find gear motors in many different applications including in many devices or appliances in your home.
Gear motors are complete motive force systems consisting of an electric motor and a reduction gear train integrated into one easy-to-mount and easy to configure package.
Due to the advantage of high torque at relatively low shaft speed or RPM, the use of gear motor greatly reduces the complexity and cost of designing and constructing power tools, machines and appliances.
Gear motors allow the use of economical low-horsepower motors to provide great motive force at low speed such as in lifts, winches, medical tables, jacks and robotics.
DC gear motor can be designed large enough to lift a building or small enough to drive a tiny clock.
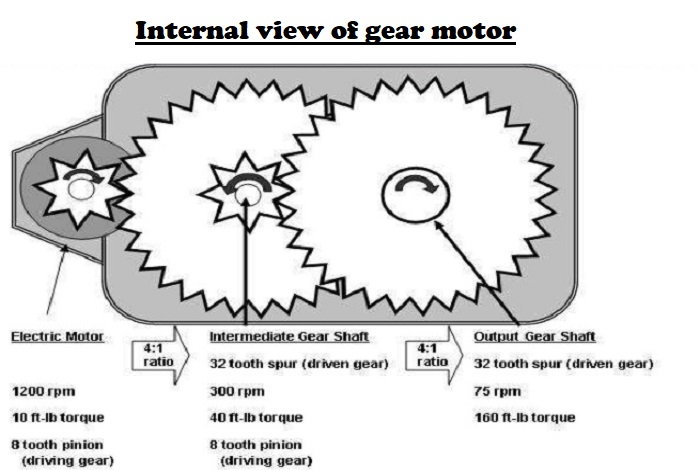
Gear Motor Operating Principle
Most synchronous AC electric motors have output ranges from 1,200 to 3,600 revolutions per minute.
They also have both normal speed and stall-speed torque specifications.
The reduction gear trains used in gear motors are designed to reduce the output speed while increasing the torque.
The increase in torque is inversely proportional to the reduction in speed.
Reduction gearing allows small electric motors to move large driven loads, although more slowly than larger electric motors.
Reduction gears consist of a small gear driving a larger gear. There may be several sets of these reduction gear sets in a reduction gear box.
types of gear motor
Most industrial gear motors are AC-powered, fixed-speed devices, although there are fixed- gear-ratio, variable-speed motors that provide a greater degree of control.
DC gear motors are used primarily in automotive applications such as power winches on trucks, windshield wiper motors and power seat or power window motors. DC motors are used more as compared to AC motors for the application of gears. Other types of gear motor include:
- Helical gear motor
- Shaft mounted gear motor
- Bevel-geared motor
- Worm geared motor
External Gear Motor consists of 2 rotating gears. The area of gear teeth is where the pressure acts to create force and both gears turn simultaneously. One gear is connected to the output shaft and the other is an idler.
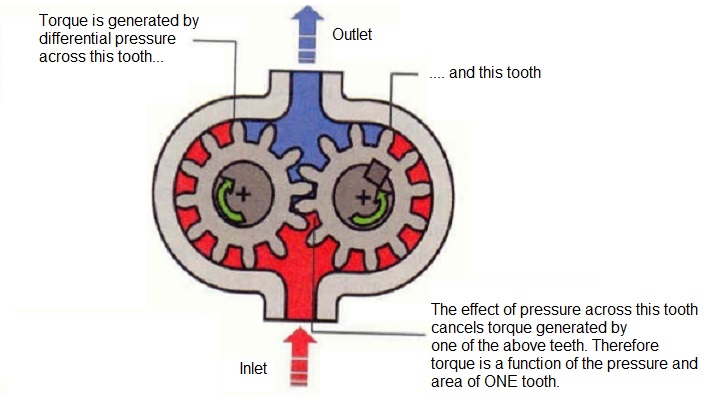
In the case of internal gear motors, direct drive rotor, works much like a rotary engine. These motors have two gears, an inner and an outer. In order to turn the shaft, the pressure pushes them around a center point.
Features of DC and Gear Motors
Some of the salient features that dc motor possesses are:
- Available in brush type and brushless motor modules.
- It is used popularly during motor sizing.
- It is a figure of merit of the motor power-to-torque ratio.
- Contains sealed bearings with high-temperature grease.
- High-temperature moulded field insulator.
- Heavy-duty commutator construction.
- Equipped with high-efficiency.
- High-flow die cast aluminium fan.
- Patented Design.
On the other hand, features of gear motors include:
- Available in standard gear mechanism
- Available in non lubricated metal bearing gear mechanism
- Also, available in planetary gear mechanism
- Provides speed reduction by the means of a gear box
- Increases the torque ratio
- Provides protection against overload and locked rotor
- Serves as protection against RFI/EMI caused by PWM control
- Used as precautions for instantaneous reversing and dynamic braking
- Used in speed detection and control
Benefits of Gear Motor
The main aim of using gear motor are:
Everything in one box
Easy to Control
Wide range of sizes, speeds and options
Mounting
Durability
Broad Purpose of Gear Motor
Speed Reduction:
Sometimes the goal of using a gear motor is to reduce the rotating shaft speed of a motor in the device being driven.
For example in a small electric clock where the tiny synchronous motor may be spinning at 1,200 rpm but is reduced to one rpm to drive the second hand. Further reduced in the clock mechanism to drive the minute and hour hands.
Here the amount of driving force is irrelevant as long as it is sufficient to overcome the frictional effects of the clock mechanism.
Torque Multiplication:
Another goal achievable with a gear motor is to use a small motor to generate a very large force albeit at a low speed.
This gear motor application includes the lifting mechanisms on hospital beds, power recliners, and heavy machine lifts where the great force at low speed is the goal.
Gear Motor Application
Garage door openers, stair lifts, rotisserie motors, timer cycle knobs on washing machines, power drills, cake mixers and electromechanical clocks have in common is that they all use various integrations of gear motors to derive a large force from a relatively small electric motor at a manageable speed.
In industry, gear motor applications in jacks, cranes, lifts, clamping, robotics, conveyance and mixing are too numerous to count.
Gear Motors are also used in these below devices:
- Coin Changing equipment
- Redemption Games
- Pinball Machines
- Peristaltic Pumps
- Food Service Equipment
- Valve Actuators
- Damper Actuators
- Pitching Machines
- Auger Motors
- Label and Packaging Equipment
- Oil Skimmers
- Fan Oscillators
- Lubricating Equipment
- Vending Equipment
Factor to consider when purchasing a 12C DC Gear Motor
There are a number of factors to consider when purchasing 12v dc gear motors. Of course you need to ensure that the design of motor you choose is fit for the job.
A gear motor has a gear reduction system or gearbox built into the motor.
In addition to ensuring that the gearbox is high quality and durable, you also want to ensure that the motor:
- Can handle the work you need done, will operate at the right speed and use the right amount of power for the job
- Type of power source is right for you. Purchasing the wrong type of motor may mean you need to replace your power source
- Can work within the conditions. You may need to use the motor for long periods of time without it overheating, or use it in less than ideal weather conditions. Make sure the gear motor you choose can handle the conditions and strain you’ll put it under.
- Has the right operating power
- Has the right amount of power to perform the job
How to Cut the Gear Motor Cost
Cost is always an important consideration of any purchase. A great way to cut costs while still purchasing a high-quality, reliable and durable 12v dc gear motor is to contact a local distributor.
Ideally, you want to find a gear motor with the specifications you need for an affordable price.
The best approach is to ask your local distributor for help. Give them the specifications you’re looking for (nominal current, nominal speed, continuous torque and breakaway torque).
Distributors can find products that meet your specific requirements and since they sell through the aftermarket they can also find you the best price.
Of course you need to do your due diligence and research the 12v gear motor you’re looking for.
Once you know what you want you should shop around and do a number of price comparisons.
Take the results of your search to your local distributor to see if they can offer a better deal to buy a 12c dc gear motor.
Discover more from Electrical Engineering 123
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

