Now a days all of us use some form of batteries i.e. in mobile phones, clocks and toys etc. Battery is a device that converts chemical energy to electrical energy. We shall see more detail about battery history on this page.
In our daily life, we generally use two types of batteries, one of them is which can be used once until it gets totally discharged. Therefore we have to dispose that batteries. While another type of battery is rechargeable battery that is useful for longer periods and multiple times by recharging from external source. The former is called primary battery and the later is called secondary battery.
Sizes of Batteries
Batteries can be found in different sizes. A battery may be as small as a shirt button or may be so big in size that a whole room will be required to install a battery bank. With this variation of sizes, the battery is used anywhere from small wrist watches to a large ship.
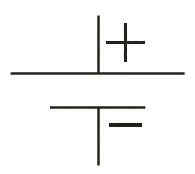
Battery Symbol
We often see this symbol in many diagrams of electrical and electronics network. This is the most popularly used symbol for battery. The bigger lines represent positive terminal of the cells and smaller lines represent negative terminal of the cells connected in the battery .
We are often confused about the terms battery cell and battery . We generally refer a battery as a single electro-chemical cell. But literally, battery does not mean that. Battery means a number of electro-chemical cells connected together to meet a certain voltage and electric current level. Although there may be a single cell battery, literally, battery and cell are different.
Battery History
The first battery was developed by Alessandro Volta in the year of 1800. In the year 1836, John Frederic Daniell, a British chemist developed the Daniell cell as an improved version of the voltaic cell. From that time until today, the battery has been the most popular source of electricity in many daily life applications.
Battery history have been very interesting which you can also understand by reading below examples about the battery evolution. In the year of 1936 during the middle of summer, an ancient tomb was discovered during construction of a new railway line near Bagdad city in Iraq. The relics found in that tomb were about 2000 years old. Among these relics, there were some clay jars or vessels which were sealed at the top with pitch.
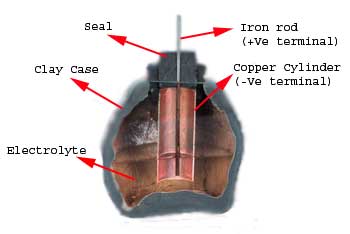
Parthian Battery
An iron rod, surrounded by a cylindrical tube made of wrapped copper sheet was projected out from this sealed top. When these pots were filled with an acidic liquid, they produced a potential difference of around 2 volts between the iron and copper. These clay jars are suspected to be 2000 year old battery cells.
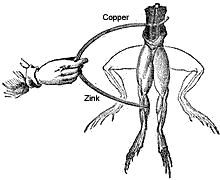
Luigi Galvani experiment with frogs legs
In 1786, Luigi Galvani, an Italian anatomist and physiologist was surprised to see that when he touched a dead frog’s leg with two different metals, the muscles of the legs contracted. He could not understand the actual reason why, otherwise he would have been known as the first inventor of the battery cell. He thought the reaction might be due to a property of the tissues.

Voltaic Pile
After that, Alessandro Volta realized that same phenomenon could be created by using cardboard soaked in salt water instead of frog’s leg. He sandwiched a copper disc and a zinc disc with a piece of cardboard soaked in salt water in between them and found a potential difference between the copper and zinc. After that in 1800, he developed the first Voltaic Pile (battery) constructed of alternating copper and zinc discs with pieces of cardboard soaked in brine between them. This system could produce measurable current. Alessandro Volta’s voltaic pile was considered the first “wet batterycell”. Thus, the history of battery began.
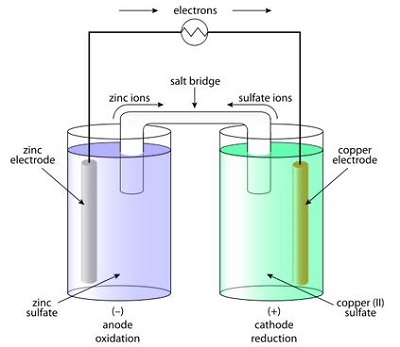
Daniell Cell
The main problem with the Voltaic pile was that, it could not deliver electric current for a long time. This problem was solved by a British inventor John F. Daniell in 1836. He invented a more developed version of the battery cell which is known as the Daniell cell. Here in this cell, one zinc rod is immersed in zinc sulfate in one container and one copper rod is immersed in copper (II) sulfate in another container. The solutions of these two containers are bridged by a U shaped salt bridge. A Daniell cell could produce 1.1 volt and this type of battery lasted much longer than the Voltaic pile.
In 1839, the fuel cell was designed by Sir William Robert Grove, a discoverer and man of science. He mixed hydrogen and oxygen within an electrolyte solution, and created electricity and water. The fuel cell did not deliver enough electricity, but it is helpful.
Bunsen (1842) and Grove (1839) created enhancements to battery that used liquid electrodes to supply electricity.

Lead Acid Battery
In the year of 1859, Gaston Plante; first developed the lead acid battery cell. This was the first form of rechargeable secondary battery. The lead acid battery is still in use for many industrial purposes. It is still the most popular to be used as car battery .
In 1866, the battery was again developed by a French engineer, Georges Leclanche. It was a carbon-zinc wet cell battery known as the Leclanche cell. Crushed manganese dioxide mixed with a bit of carbon forms the positive electrode and a zinc rod is used as the negative electrode. Ammonium chloride solution is used as a liquid electrolyte. After some years, Georges Leclanche himself improved his own design by replacing liquid ammonium chloride solution with ammonium chloride. This was the invention of the first dry cell.
In 1901, Thomas Alva Edison discovered the alkaline accumulator. Thomas Edison’s basic cell had iron as the anode material (-) and nickel oxide as the cathode material(+). This is just one portion of an endless history of battery .
Step by Step Evolution of Batteries
| DEVELOPER/INVENTOR | COUNTRY | YEAR | INVENTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| Luigi Galvani | Italy | 1786 | Animal Electricity |
| Alessandro Volta | Italy | 1800 | Voltaic Pile |
| John F. Daniell | Britain | 1836 | Daniell Cell |
| Sir William Robert Grove | Britain | 1839 | Fuel Cell |
| Robert Bunsen | German | 1842 | used liquid electrodes to supply electricity |
| Gaston Plante | France | 1859 | Lead Acid Battery |
| Georges Leclanche | France | 1866 | Leclanche Cell |
| Thomas Alva Edison | United States | 1901 | Alkaline Accumulator |
