Sinusoidal Voltage Equation
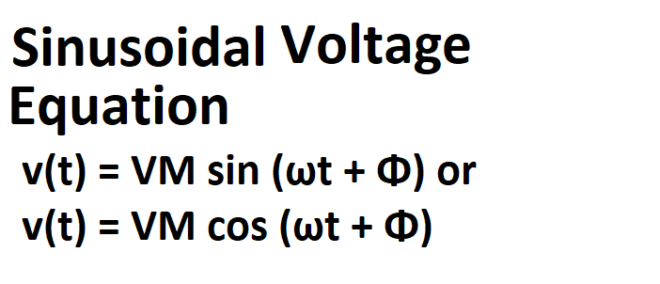
A sinusoidal voltage can be described by the equation: v(t) = VM sin (ωt + Φ) or v(t) = VM cos (ωt + Φ) where v(t) Instantaneous value of the voltage, in volts (V). VM Maximum or peak value of the voltage,
Resources For Electrical & Electronic Engineers
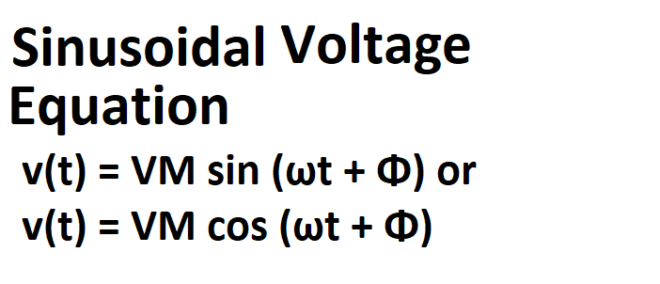
A sinusoidal voltage can be described by the equation: v(t) = VM sin (ωt + Φ) or v(t) = VM cos (ωt + Φ) where v(t) Instantaneous value of the voltage, in volts (V). VM Maximum or peak value of the voltage,
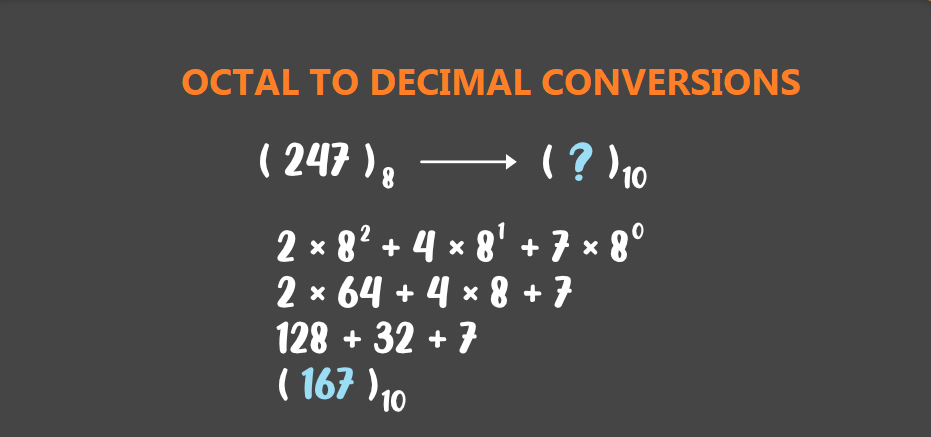
The Octal Number System is another type of computer and digital base number system. Octal Number System is very similar in principle to the previous hexadecimal numbering system except that in Octal, a binary number is divided up into groups of only

On this page you can find information about the circuit breaker types or classification by the interrupting medium used i.e. oil, air, vacuum or gas etc. Oil Circuit Breakers Oil has an excellent dielectric strength which enables itself not only to be

Below you can find MCQ’s or Multiple Choice Questions related to the Transmission Lines in the field of Communications Engineering. Correct answers are in red & bold font. 1. What determines the velocity factor in transmission line? a) The termination impedance b)

Section 1: Electrical interview questions and answers about switchgear and protection What are the functions of protective relays? To detect the fault and initiate the operation of the circuit breaker to isolate the defective element from the rest of the system, thereby
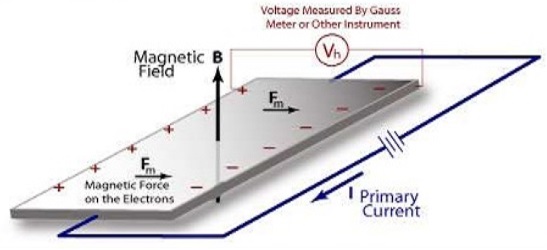
The Hall effect was discovered 18 years before the discovery of electrons i.e. in 1879 by Edwin Herbert Hall. This achievement happened when he was working on his doctoral degree at the Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, Maryland, USA. What is Hall