Brushless motor also known as BLDC motor is a synchronous motor that gets power by a DC electric source. It uses an integrated inverter, which ultimately produces an AC electric signal to drive the motor.
British scientist Michael Faraday first experimented with the idea of the electromagnetic induction motor in the early 1800’s.
During that time, DC Motors did not contain permanent magnets. Instead, they operated similar to Brush DC Motors today, in that they had current flowing through the windings of the motor.
In 1837 Americans Thomas and Emily Davenport transformed Faraday’s DC Motor into one that could be used for commercial use.
These DC Motors became popular in printing presses and powered machine tools.
Principle of Brushless Motor
BLDC motor is simply a normal dc motor turned inside out, that means the coil is on the outer side and the magnets are inside.
The stator consists of several coils in which current is led through. Hence creating a magnetic field that makes the rotor turn.
Unlike a brushed DC motor, the commutation of a BLDC motor is controlled electronically.
It is important to know the rotor position in order to understand which winding will be energized following the energizing sequence.
Rotor position is sensed by different ways some of them are hall sensors and optical encoders.
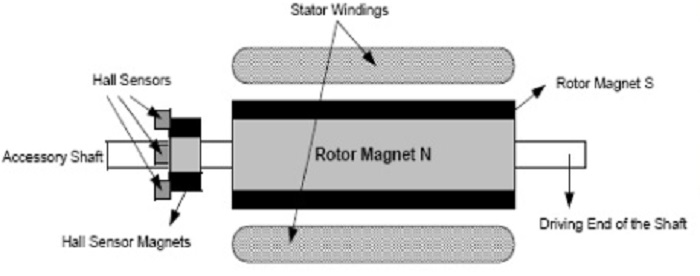
When a magnetic field applied to a system with electric current a hall voltage Perpendicular to the field and to current is generated. This was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879, known as hall effect.
Operation of Brushless BLDC Motor
The operation of a BLDC is based on the simple force interaction between the permanent magnet and the electromagnet.
In this condition, when the coil A is energized, the opposite poles of the rotor and stator are attracted to each other (The attractive force is shown in green arrow). This results the rotor poles move near to the energized stator.
When the rotor nears coil A, coil B is energized. As the rotor nears coil B, coil C is energized. After that, coil A is energized with the opposite polarity.
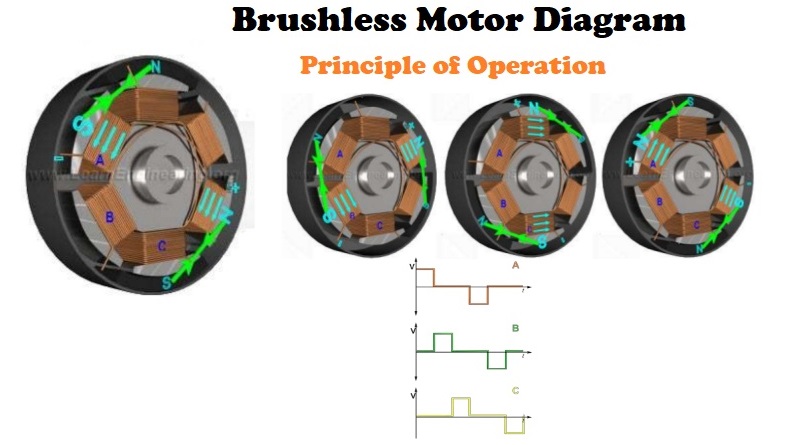
This process is repeated, and the rotor continues to rotate.
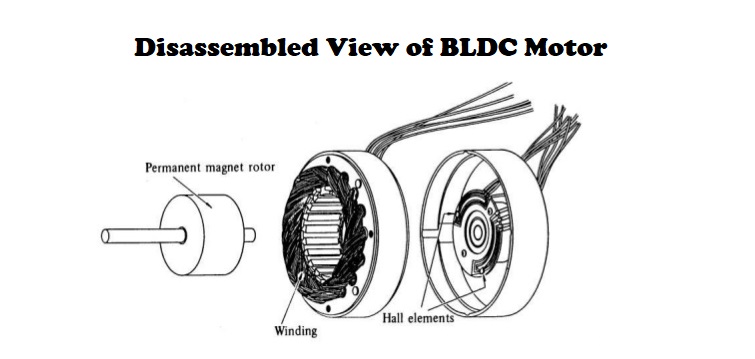
Construction of Brushless DC Motor
Brushless motor consists of mainly two parts; stator & rotor.
The bldc motor stator consists of stacked steel laminations with windings placed in the slots that are axially cut along the inner periphery. Stator is made up of silicon steel stamping with slots. The slots accommodate in armature windings.
This winding is wound with specified no.of poles(even number). This winding is connected to a dc supply through a power electronic switching circuits ( inverter circuits) .
Rotor is made of permanent magnet and can vary from two to eight pole pairs with alternate North (N) and South (S) poles. Ferrite magnets and Rare earth alloy magnets are used in rotor construction. Number of poles on rotor is same as that of stator.
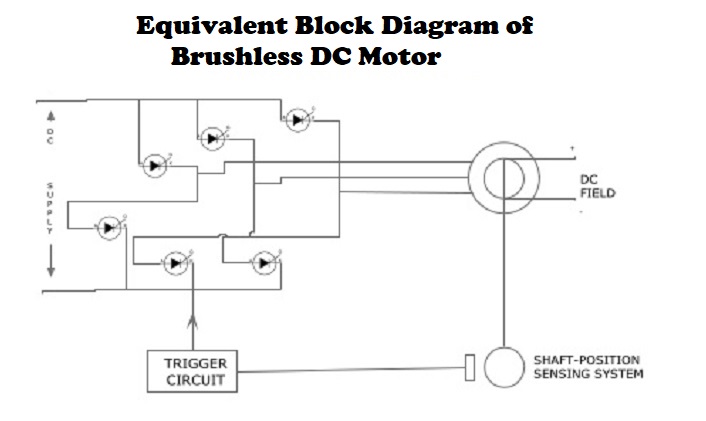
Rotor shaft carries a RPS (Rotor position sensor) and it provides information about the position of shaft at any instant to the controller which sends signal to the electronic commutator .
The electronic commutator function is same as that of mechanical commutator in DC motor.
Advantages of Brushless Motor
- Increased Reliability & Efficiency
- Maintenance free
- Explosion free
- No risk of RF radiation due to arcing
- Longer Life
- Elimination of sparks from Commutator
- Reduced Friction
- Faster Rate of Voltage & Current
- Rapid response
Disadvantages of Brushless DC Motor
- Requires Complex Drive Circuitry
- Requires additional Sensors
- Higher Cost
- Some designs require manual labor (Hand wound Stator Coils)
Brushless DC Motor Applications
Consumer: Hard Drives, CD/DVD Drives, PC Cooling Fans, toys, RC airplanes, air conditioners
Medical: Artificial heart, Microscopes, centrifuges, Arthroscopic surgical tools, Dental surgical tools and Organ transport pump system.
Vehicles: electronic power steering ,personal electric vehicles
Airplanes: an electric self launching sailplane, flies with a 42kW DC/DC brushless motor and Li-Ion batteries and can climb up to 3000m with fully charged cells
Factory automation systems
Aerospace industry
Military
Conclusion
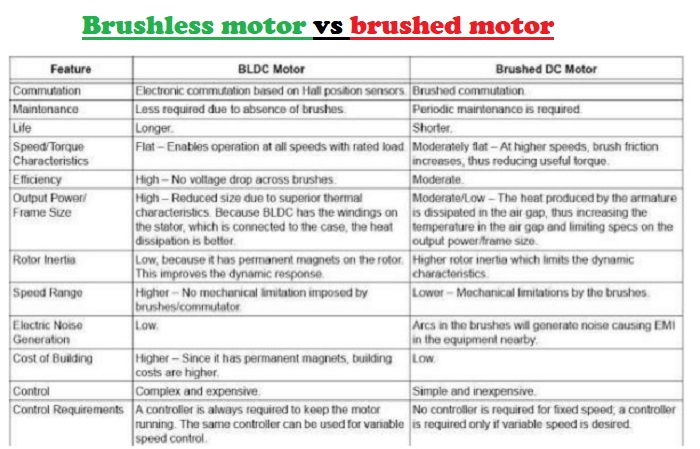
Although Brushless Motors are more expensive of the same kW rating than conventional DC Motor but there are many advantages.
Brushless DC Motors can run when submerged in fluids.
BLDC Motor does not produce brush or commutator particles or gases as by-products of operation if we compare brushless motor vs brushed one.
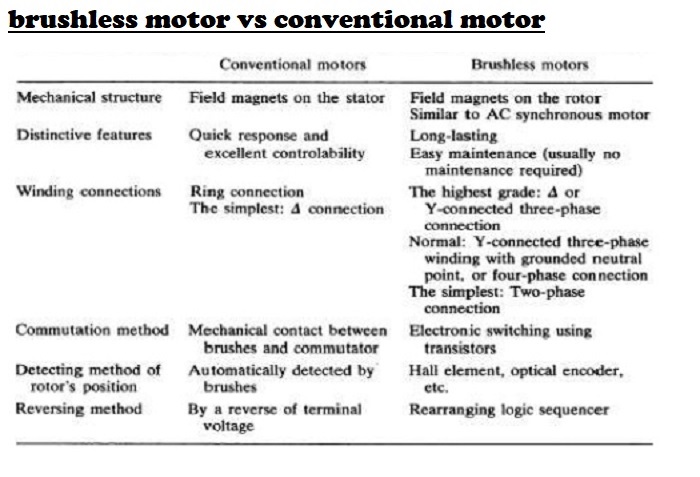
Brushless Motor vs Brushed Motor
Discover more from Electrical Engineering 123
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
