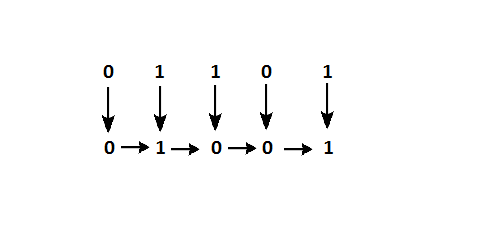
Gray Code is one of the most important codes. It is a non-weighted code which belongs to a class of codes called minimum change codes. In this codes while traversing from one step to another step only one bit in the code
Read More
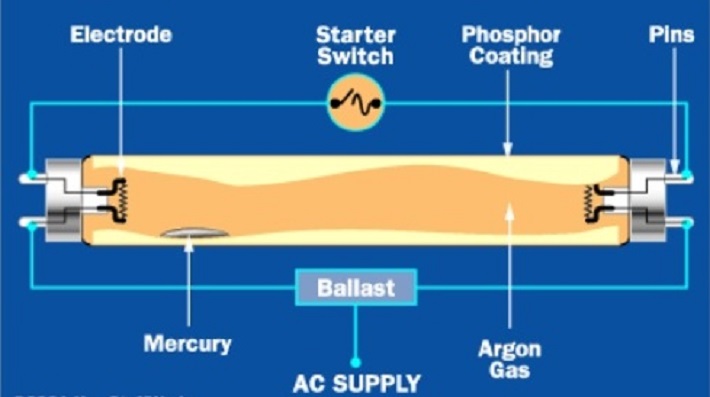
Fluorescent light electronic ballast provides initial high voltage for discharging the gas inside the fluorescent lamps/bulbs. Ballast converts power frequency to very high frequency that initializes gas discharge process by controlling voltage and current through the lamps. There are different types of light
Read More
The electrical energy is almost exclusively generated, transmitted and distributed in the form of alternating current. Therefore, the question of power factor immediately comes into picture. Most of the loads (e.g. induction motors, arc lamps) are inductive in nature and hence have
Read More
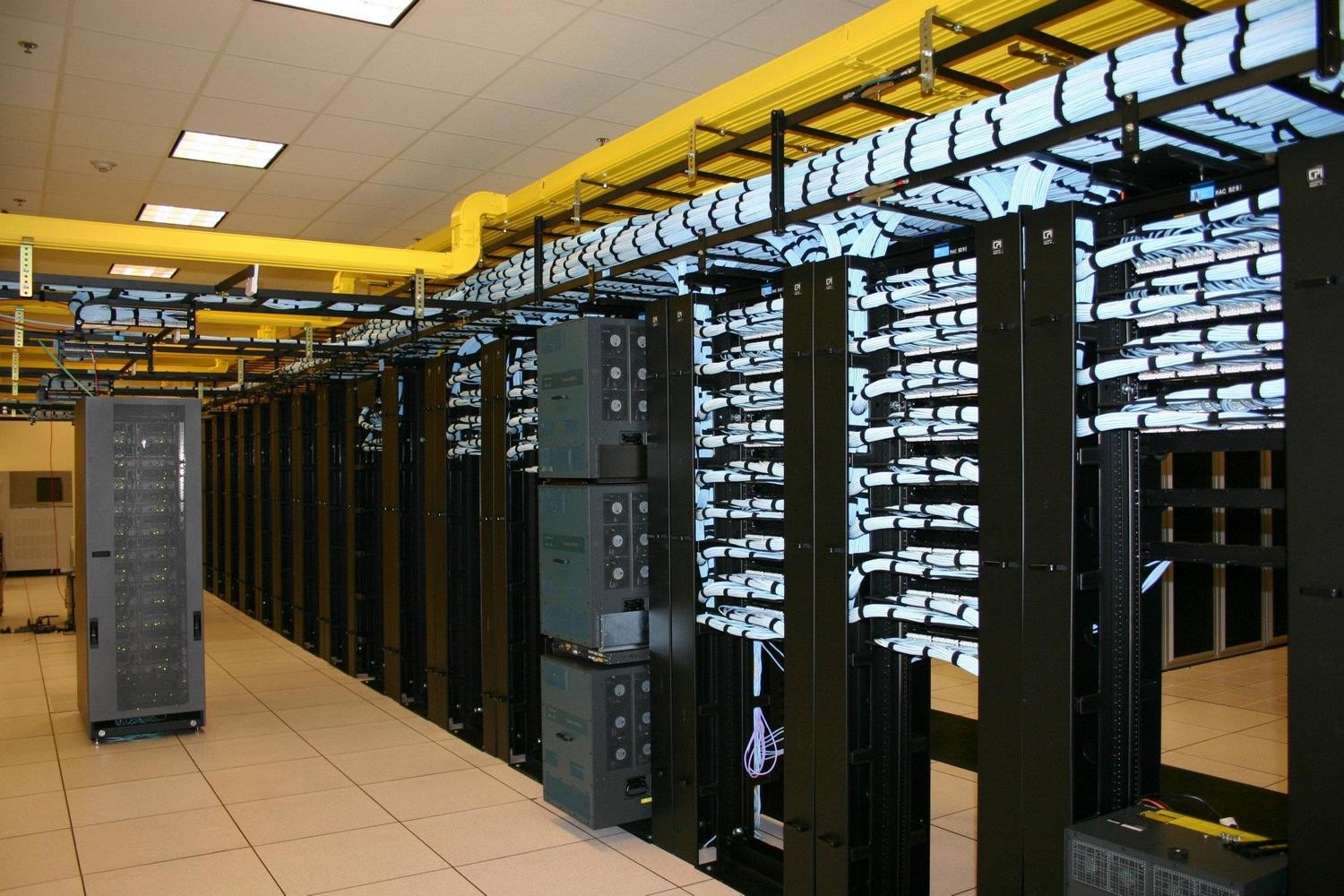
All material used at the project site shall be approved prior to the start of IP Telephony system installation works. Materials and documentation relevant to a particular section of works will be checked by the site/project engineer prior to the commencement of
Read More
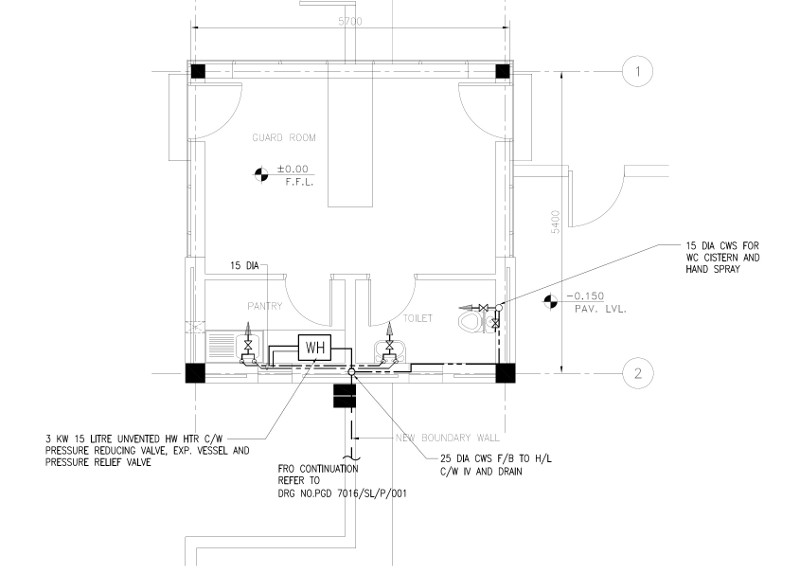
If you have recently put yourself in engineering field or you are interested to know the latest technology in drafting then this page might be helpful for you. In past around 20-25 years back it was a big task to generate new
Read More
A contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching an electrical power circuit , similar to a relay except with higher current ratings. Contactor is in fact an electromechanical switch. Low-voltage Contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching an
Read More