Dielectric Materials A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only
Read More
What is a Capacitor? Capacitor is a device that stores electric charge. A capacitor consists of two conductors separated by an insulator. Capacitors have many applications some of them include Computer RAM memory and keyboards, Electronic flashes for cameras, Electric power surge
Read More
What is Electronics? Electronics can be defined as the science of how to control electric energy, electrical energy is the form of energy in which the electrons have a fundamental role. The field of basic electronic also deals with electrical circuits which involve active
Read More
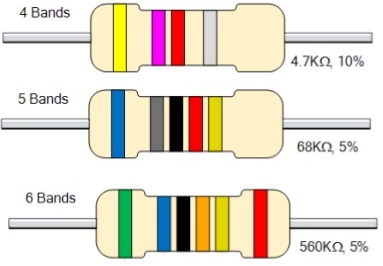
If you want to understand resistor color coding then you are at right place where you are explained full resistor calculator depending upon the resistor color bands which are always confusing for the electricians. There are 4, 5 and 6 bands on
Read More
DHT11 & DHT22 temperature & humidity sensor are well known models which are used for monitoring the humidity and temperature of a vicinity or place. DHT11 and DHT22 models are used in thermostats and hygro thermometers which are used for different purposes
Read More
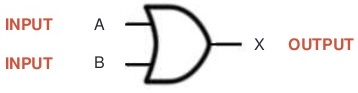
Gates are mainly the subject of digital logic designing profession which is a very basic and important section of digital world. In fact term logic is applied to digital circuits in order to implement the logic functions. There are many types of
Read More