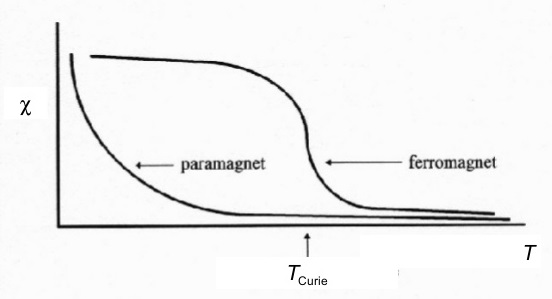
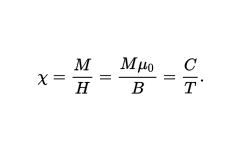Spontaneous magnetization is the appearance of an ordered spin state (magnetization) at zero applied magnetic field in a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material below acritical point called the Curie temperature or TC. Heated to temperatures above TC, ferromagnetic materials become paramagnetic and their
Read More
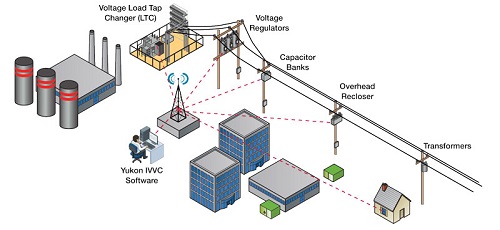
Distributions systems represent an important parts in the electrical grids and for this reasons the electrical generation & distribution companies delicate approximately 40% of the capital investment for distribution systems while the remaining is given to generation and transmission (40% generation &
Read More
In a paramagnetic material the magnetization of the material is (approximately) directly proportional to an applied magnetic field. However, if the material is heated, this proportionality is reduced; for a fixed value of the field, the magnetization is (approximately) inversely proportional to
Read More
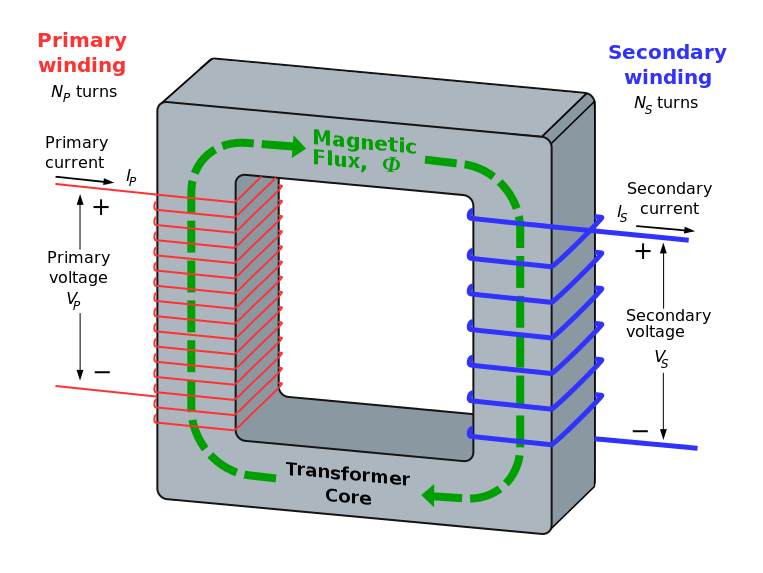
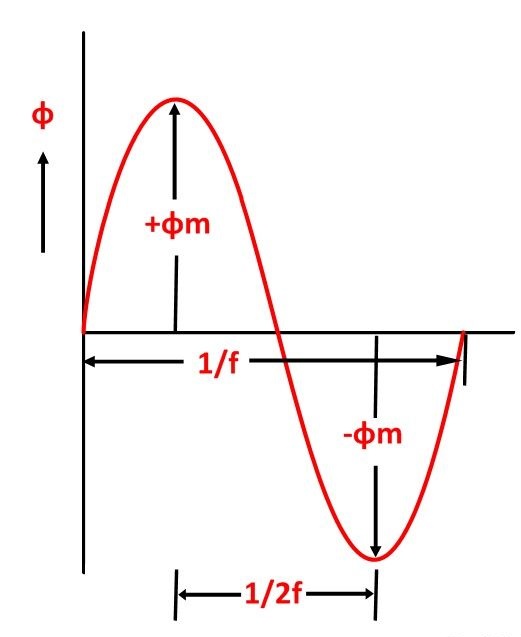
An ideal transformer is a theoretical, linear transformer that is lossless and perfectly coupled; that is, there are no energy losses and flux is completely confined within the magnetic core. Perfect coupling implies infinitely high core magnetic permeability and winding inductance and zero
Read More
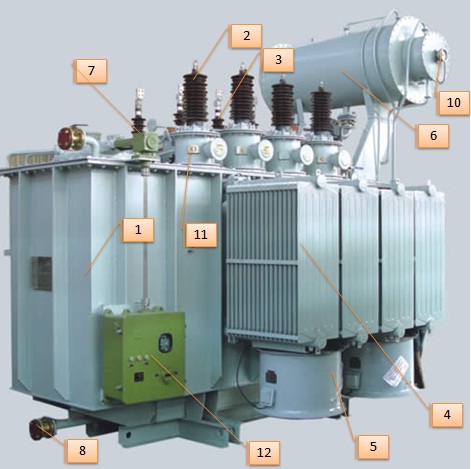
In general understanding electrical distribution transformers are used to reduce primary system voltages (which is normally 2.4-34.5kV) to the level of utilization voltages i.e. 120- 600V. International electrotechnical commission standards do not distinguish between distribution electrical transformers and power transformer. They are
Read More
Power transformer is most costly and essential equipment of an electrical system. It is well known fact that power transformers are the heart of the power systems which enables to establish very large power systems networks. Failure of any transformer will create
Read More