What is an ELCB? An Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker (ELCB) is a safety device used in electrical installations with high earth impedance to prevent shock. It detects small stray voltages on the metal enclosures of electrical equipment, and interrupts the circuit if
Read More
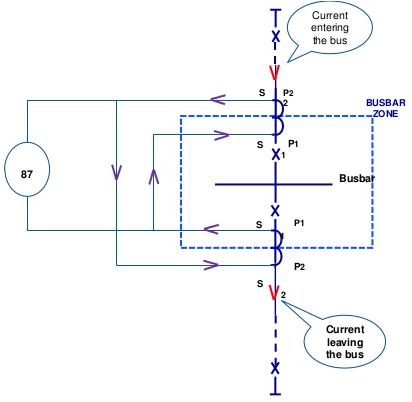
Before discussing the types and importance of busbar protections let’s see what is a bus bar? The word bus is derived from Latin word “OMNIBUS” that means common for all, so busbar is actually a common and main part of a power
Read More
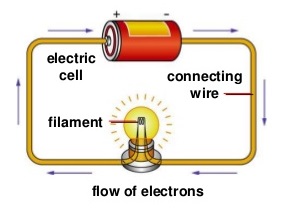
What is Electricity? Electricity is a form of energy that can be easily changed to other forms. Electricity comes mainly from 2 sources i.e. Power stations and generators that supply a lot of electricity and normally used in many electrical appliances and industrial
Read More
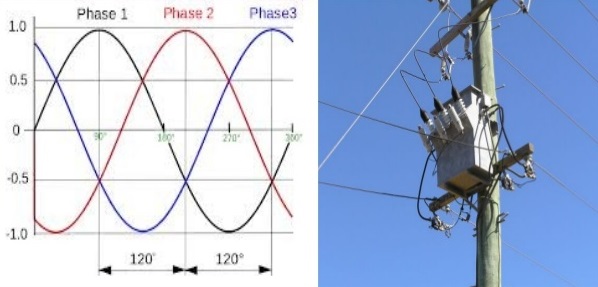
Single Phase power circuits Single phase electric power or circuit refers to the distribution of alternating current electric power using a system in which all the voltages of the supply vary in corresponding exactly. Single-phase distribution is used when loads are mostly
Read More
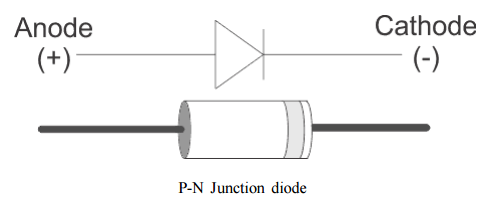
What is a Diode? Di+Ode is a semiconductor device with two terminals allowing the flow of current in one direction only, diodes are made up of Silicon, Germanium & GaAs. The perfect diode would be a perfect conductor in one direction (forward bias) and
Read More
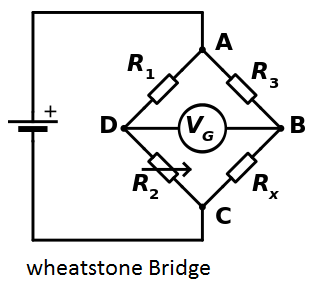
What is the Wheatstone Bridge? The Wheatstone Bridge consists of a dc voltage source, four resistors and a detector. The detector is a type of ammeter called a galvanometer. The galvanometer is used to detect the condition ig = 0 .When the circuit
Read More